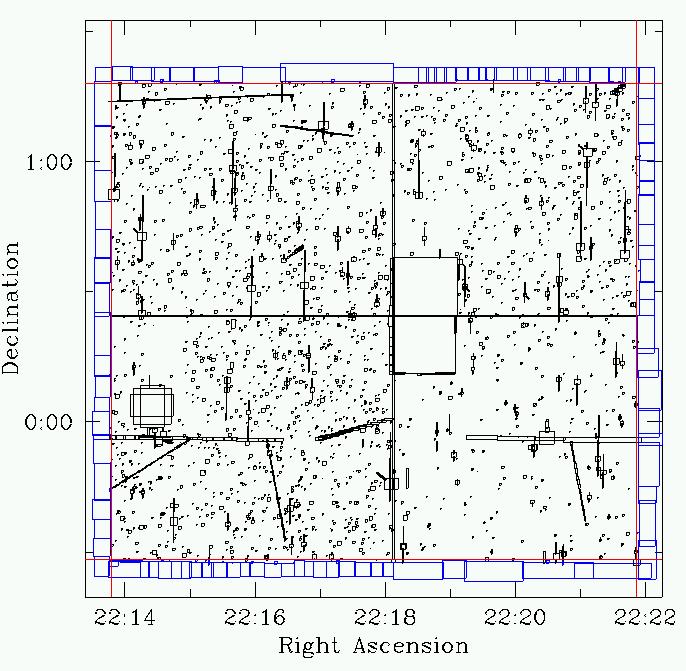
The boundaries of the field are shown in red.The boxes shown in blue may be ignored, as they lie outside the boundaries.
| Summary:
This page describes the F22I wide catalog. It gives: |
Description of catalogs:The relevant files:Some of these files (for reasons of convenience) are available as links from this page. Others are only available on the VIRMOS disk.
Sky area:A rectangle between:
With allowances for the masked areas, the total area is: 3.345 square degrees. Masking:The following areas were masked:
|
| The figure at right shows the layout of the
masks in the file F22I.boxes. The large box near the centre was not observed.
The patch at lower left is an extremely bright star which causes an unacceptable
number of false detections.
The boundaries of the field are shown in red.The boxes shown in blue may be ignored, as they lie outside the boundaries. |
 |
Notes on reduction procedures:This section provides a brief reference for the data reduction procedure.
|
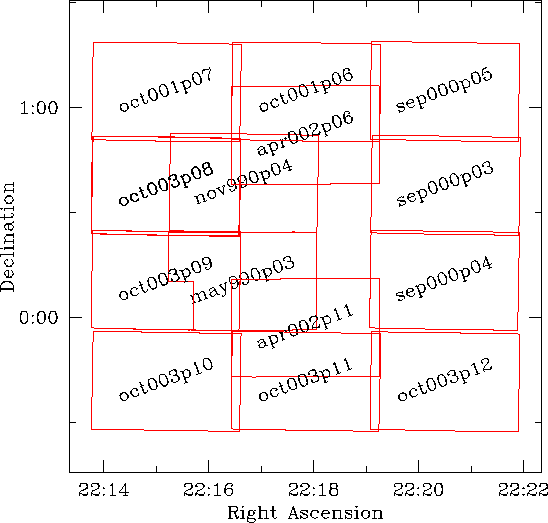
| The figure at right shows the layout of the observations.
They are labelled as follows:
oct003p09
Note that the outlines of the observations are determined directly the astrometrically calibrated data frames. |
 |
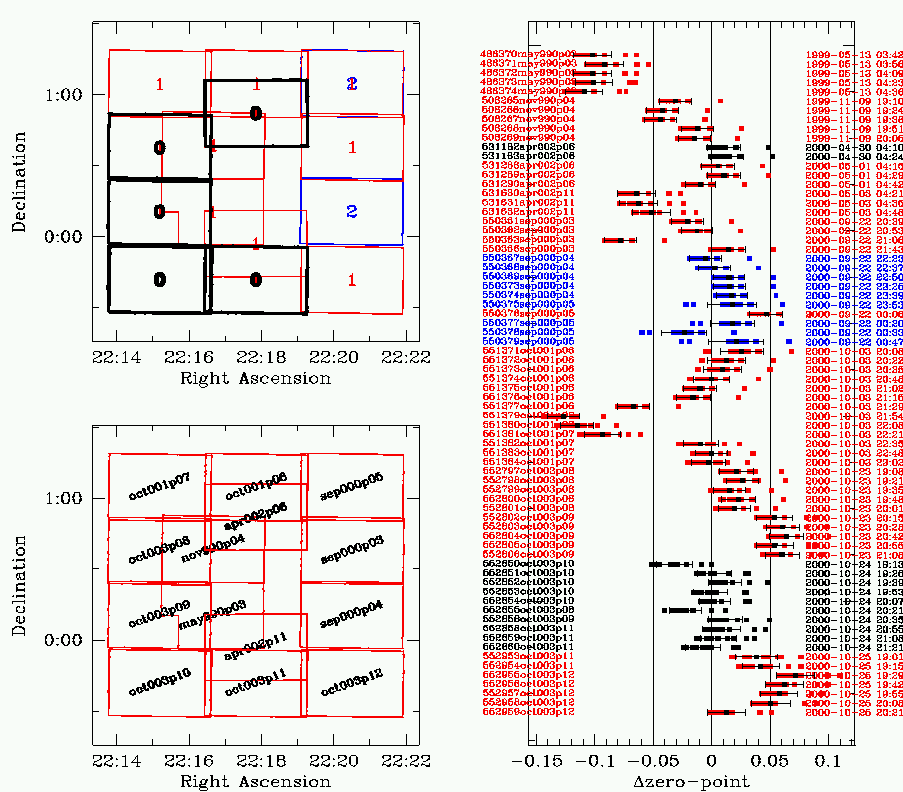
| The figure at right shows how the photometric calibration
was done.
Lower left: layout of the 22hr pointings, outlined in red and labelled in black. Upper left: layout of the 22hr pointings. Photometric exposures are
in heavy black and labelled "0". Exposures that "touch" (more than 150
common objects) photometric exposures are in red and labelled "1". Exposures
that "touch" level 1 exposures are outlined in blue and
Big right panel: For every exposure, a zero-point was calculated under the (usually erroneous) assumption that it was taken under photometric conditions. This zero-point was calculated using using the airmass and exposure time from the header and the zero-point for the run. This zero-point is known as the "nominal" or "original" zero-point. Some exposures were flagged as being genuinely photometric. These ones
are shown in black. For each photometric exposure, zero-points for all
the other exposures by comparing magnitudes in the overlap regions. The
difference between this "calculated" zero-point and the "nominal" one is
plotted along the x-axis.
The final zero-point for each exposure is the average of the all the "calculated" zero-points for that exposure. |
 |
| Data tests: |
| The figure at right shows the I band galaxy number counts for the F22I together with several data from the literature. | 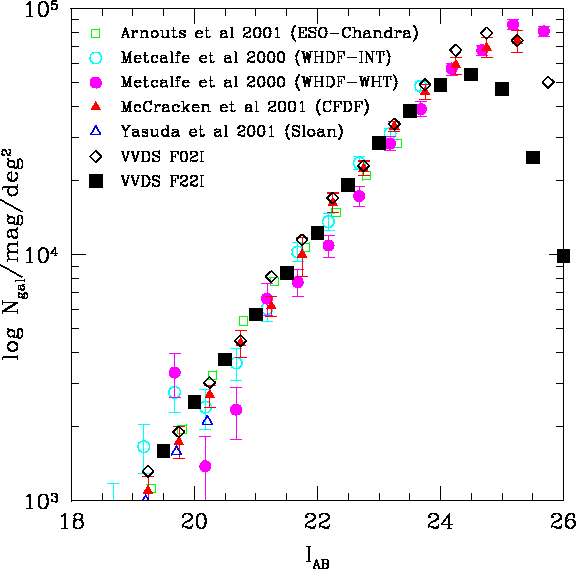 |